Enchanted Learning Resources Overview
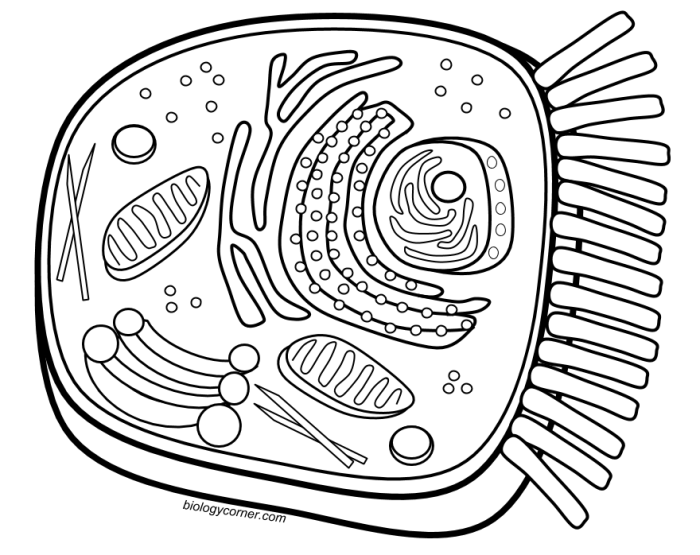
Enchanted learning animal and plant cell coloring – Enchanted Learning offers a valuable collection of educational resources for children, particularly in the areas of science and language arts. Their website presents information in an engaging and visually appealing manner, making learning more accessible and enjoyable for young learners. The site’s strength lies in its ability to combine clear explanations with vibrant illustrations and interactive elements, fostering a deeper understanding of complex concepts.The pedagogical approach employed in Enchanted Learning’s animal and plant cell materials emphasizes visual learning and interactive exploration.
Enchanted Learning’s animal and plant cell coloring pages offer a fantastic way to learn biology through creative engagement. For a slightly different approach, after completing those detailed cell structures, you might enjoy a simpler activity like coloring some adorable penguins; check out these easy animal coloring pages penguin for a fun break. Returning to the more complex world of cells, remember that understanding cell structures is key to understanding life itself.
The resources utilize colorful diagrams and illustrations to depict the structures and functions of cells, breaking down complex biological processes into easily digestible components. Children are encouraged to actively engage with the material through interactive exercises, such as labeling diagrams and answering questions, reinforcing their learning through active participation. This approach aligns with constructivist learning theories, which emphasize the importance of active learning and knowledge construction.
Comparison with Other Online Educational Resources
Enchanted Learning distinguishes itself from other online educational resources through its unique blend of visual appeal and clear, concise explanations. While many online resources provide factual information, Enchanted Learning excels in presenting this information in a visually engaging format that caters to younger learners’ attention spans and learning styles. Other sites might rely heavily on text-based learning or lack the interactive elements that make Enchanted Learning’s materials so effective.
For instance, a purely text-based explanation of cellular respiration might be challenging for a young child to grasp, whereas Enchanted Learning’s visual aids and interactive components can make the process much clearer. Furthermore, while some educational websites focus on specific curriculum standards, Enchanted Learning provides a broader range of engaging topics, encouraging exploration beyond the confines of a typical school syllabus.
This breadth of content allows children to pursue their individual interests and deepen their understanding of various subjects.
Analysis of the “Animal and Plant Cell Coloring” Activity
The “Animal and Plant Cell Coloring” activity from Enchanted Learning offers a visually engaging and interactive method for students to learn about the fundamental structures of animal and plant cells. This hands-on approach effectively complements traditional learning methods, fostering deeper comprehension and retention of key biological concepts.The coloring activity facilitates learning by combining visual representation with active engagement. Students are not passively receiving information; they are actively participating in the construction of their understanding of cell structures.
This active process strengthens memory and promotes a more thorough grasp of the subject matter.
Learning Objectives Achieved
This activity directly addresses several key learning objectives. Students will be able to identify and label the major organelles of both animal and plant cells. They will also develop an understanding of the differences in structure between these two cell types, highlighting the unique characteristics of plant cells, such as the cell wall and chloroplasts. Finally, the activity reinforces the understanding that cells are the basic building blocks of life.
Key Concepts of Animal and Plant Cell Structure Conveyed
The coloring pages effectively convey the key structural components of both animal and plant cells. For animal cells, the activity emphasizes the nucleus (containing the genetic material), the cytoplasm (the jelly-like substance filling the cell), the mitochondria (the powerhouses of the cell), the ribosomes (responsible for protein synthesis), and the cell membrane (the outer boundary of the cell). Plant cells, in addition to these components, highlight the presence of a rigid cell wall providing structural support, large central vacuoles for storage and turgor pressure, and chloroplasts, the sites of photosynthesis.
Enhanced Understanding of Cell Components Through Coloring
The act of coloring the different organelles helps students associate specific functions with their visual representations. For instance, coloring the mitochondria a vibrant color might help them remember its role in energy production. Similarly, coloring the chloroplasts green reinforces their association with photosynthesis. The visual distinction between the animal and plant cell structures, particularly the cell wall and chloroplasts in plant cells, emphasizes the functional differences between the two cell types.
The spatial arrangement of organelles within the cell, as depicted in the coloring pages, further enhances understanding of their relative positions and interactions within the cell’s environment.
Pedagogical Considerations of Coloring Activities: Enchanted Learning Animal And Plant Cell Coloring
Coloring activities, while seemingly simple, offer a surprisingly effective pedagogical approach to teaching complex biological concepts like cell structure. The act of coloring engages students in a multi-sensory learning experience, moving beyond passive observation to active participation and reinforcement of knowledge. This tactile engagement can be particularly beneficial for visual learners and those who benefit from kinesthetic learning strategies.Coloring activities provide a bridge between abstract diagrams and the three-dimensional reality of cells.
By assigning specific colors to different organelles, students create a visual representation that helps solidify their understanding of the function and location of each component. This active construction of knowledge is more effective than simply memorizing labels on a diagram or passively watching a video.
Comparison of Coloring with Other Teaching Methods
Coloring offers distinct advantages over other common teaching methods for cell structure. Diagrams, while useful for providing a visual overview, often lack the engagement and memorability of a hands-on activity. Similarly, videos can be effective, but they may not allow for the same level of individual interaction and personalized learning pace that coloring provides. Students can revisit their colored diagrams as study aids, reinforcing their learning over time.
A well-designed coloring sheet, like the Enchanted Learning example, encourages detailed observation and attention to the specific characteristics of each organelle, fostering deeper understanding than a cursory glance at a diagram or a fleeting video clip.
Integrating Coloring into Broader Lesson Plans
The coloring activity can be seamlessly integrated into a larger lesson plan on cells. For example, it could be used as an introductory activity to stimulate interest and provide a visual foundation before moving onto more complex textual material or microscopic observation. Following the coloring activity, teachers could incorporate a class discussion comparing the colored diagrams, highlighting commonalities and differences in students’ interpretations.
This fosters collaboration and critical thinking. Subsequently, a quiz or worksheet focusing on cell structures and functions could assess comprehension and reinforce learning. The colored diagrams could also serve as visual aids during further discussions about cellular processes, such as protein synthesis or cellular respiration. Finally, a project involving building 3D models of cells could further extend the learning, building upon the visual foundation established through the coloring activity.
This layered approach maximizes the educational impact of the coloring activity, transforming it from a simple exercise into a valuable component of a comprehensive learning experience.
Creating Enhanced Learning Materials
Enhancing the learning experience beyond a simple coloring activity requires incorporating complementary activities that solidify understanding and assess knowledge retention. The following sections detail an alternative activity, a short quiz, and a detailed illustration description designed to achieve these goals.
Alternative Activity: Cell Organelle Matching Game
To further reinforce learning about animal and plant cells, a matching game can be created. This game would involve creating cards with images of different cell organelles (e.g., nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplast, cell wall) and cards with descriptions of their functions. Students would match the organelle image with its corresponding function. This hands-on activity provides a more interactive and engaging way to learn about the various components of cells and their roles.
The game can be easily adapted for different age groups and learning styles by adjusting the complexity of the descriptions and images. For example, younger students could use simpler images and shorter descriptions, while older students could use more detailed images and scientific terminology.
Quiz: Assessing Understanding of Animal and Plant Cells
The following quiz assesses student comprehension after completing the coloring activity. The quiz uses a multiple-choice format and short-answer questions to gauge both factual recall and understanding of concepts.
| Question | A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Which organelle is responsible for energy production in a cell? | Nucleus | Mitochondria | Chloroplast | Cell Wall |
| Which of the following is found only in plant cells? | Mitochondria | Cell Membrane | Cytoplasm | Chloroplast |
| What is the function of the cell wall? | Energy production | Protein synthesis | Structural support and protection | Waste removal |
| What is the control center of the cell? | Ribosomes | Vacuole | Nucleus | Golgi apparatus |
| Which organelle is responsible for packaging and transporting proteins? | Endoplasmic Reticulum | Golgi Apparatus | Lysosome | Ribosome |
| Short Answer Questions | Answer Space |
|---|---|
| Describe the function of the vacuole in a plant cell. | |
| Explain one key difference between the cell membrane and the cell wall. |
Illustration Description: Animal vs. Plant Cell, Enchanted learning animal and plant cell coloring
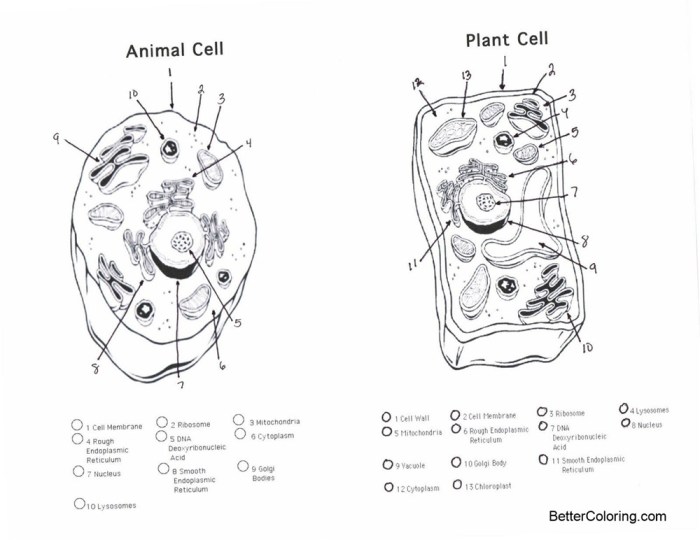
The illustration depicts a comparative view of an animal and a plant cell. Both cells are shown with their respective key organelles. The animal cell, on the left, displays a prominent nucleus, numerous mitochondria scattered throughout the cytoplasm, a Golgi apparatus, a rough endoplasmic reticulum, a smooth endoplasmic reticulum, and lysosomes. The cell is bounded by a flexible cell membrane.
The plant cell, on the right, shows similar organelles but with distinct differences. It features a large central vacuole occupying a significant portion of the cell’s volume, responsible for maintaining turgor pressure and storing nutrients. A rigid cell wall surrounds the cell membrane, providing structural support and protection. Crucially, the plant cell also contains chloroplasts, the sites of photosynthesis, which are absent in the animal cell.
The illustration uses color-coding to highlight the differences between the organelles and emphasizes the size and location of each organelle within each cell type. The illustration clearly shows the relative size differences between the organelles and the overall size difference between the two cell types. The labels for each organelle are clear and concise, using readily understandable terminology.
